Understanding Mean Reversion Trading
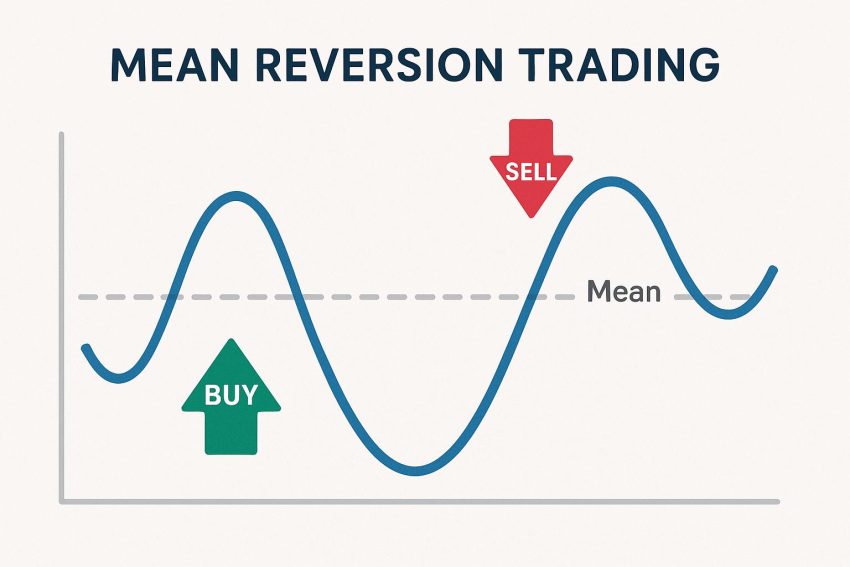
Mean reversion trading is a widely employed strategy in the world of financial trading, premised on the observation that the prices of financial instruments tend to oscillate around their average value over a specific period. This technique involves pinpointing securities whose prices have diverged from their historical average and making investment moves based on the anticipation that these prices will return to the mean. At its core, mean reversion aims to buy low and sell high, leveraging disparities in short-term price movements to achieve gains.
Basic Principles of Mean Reversion
The idea of mean reversion is anchored in statistical principles, primarily concerning the mean or average price of an asset. Traders who adopt this strategy work on the assumption that whenever prices stray considerably from their means, they are destined to hike back to average levels. This philosophy runs counter to trend-following strategies, which maintain that price trajectories are inclined to persist in their current course.
Calculating the Mean
In the practical application of mean reversion, traders calculate the mean by analyzing historical price data over a predetermined period. This investigation may involve examining data points such as closing prices, daily highs and lows, or adjusted closing prices that take dividends and stock splits into account. The chosen time frame can differ, yet some standard selections include applying a 50-day, 100-day, or 200-day moving average.
Percentage Thresholds
A crucial component of mean reversion trading involves setting percentage thresholds to gauge deviations from the mean. Traders may decide to make a purchase when a stock trades at 15% below its 100-day moving average or to sell when it rises 15% above. These predefined thresholds serve as valuable markers to determine optimal entry and exit points for investment decisions.
Implementing a Mean Reversion Strategy
Effectively executing a mean reversion strategy requires following a series of methodical steps:
Identifying Opportunities
The initial phase involves scanning for securities that have deviated from their average value. This can be streamlined using tools like stock screeners and advanced technical analysis software. Traders generally seek stocks that have demonstrated a strong historical inclination to revert to the mean, thereby allowing for more reliable anticipations of price adjustments.
Analyzing Market Conditions
Before engaging in any trades, it’s imperative to assess the overall market conditions. Mean reversion strategies are typically more effective in range-bound markets as opposed to trending ones. A comprehensive understanding of market context can substantially improve the probabilities of successful trade outcomes.
Risk Management
As is the case with any trading methodology, proficient risk management is vital. Traders should employ strategies like placing stop-loss orders to cap expected losses if the price fails to revert as anticipated. Additionally, prudent position sizing and asset diversification can further contribute to risk mitigation.
Challenges and Considerations
While mean reversion can prove to be an effective trading strategy, it is not devoid of challenges. Strong market trends can lead to extended periods of deviation from the mean, potentially resulting in significant setbacks. Moreover, traders might encounter instances where a security appears to revert to the mean but unexpectedly continues its existing trajectory.
Market Efficiency
The mean reversion approach operates on the belief that markets exhibit inefficiencies that result in temporary mispricings. However, in highly efficient markets, deviations may be insufficient to justify this strategy, particularly once the costs of transactions are taken into account.
Choosing the Right Assets
It’s critical to recognize that not every asset or market aligns favorably with a mean reversion strategy. Certain stocks or indices display heightened volatility or are driven by prevailing trends, making their reversion patterns less predictable. Hence, careful asset selection combined with continuous monitoring of asset behavior is pivotal for strategic success.
Conclusion
Mean reversion trading offers a robust framework for engaging in financial markets with the ultimate objective of buying at lower prices and selling at higher ones, all grounded in historical price patterns. While it holds the potential for profitability when applied under suitable conditions, those employing this strategy must vigilantly manage risk and stay attuned to the dynamics of market trends. An in-depth grasp of mean reversion principles and their application can substantially boost the chances of yielding favorable outcomes in trading endeavors. Adhering to these concepts while maintaining a disciplined approach can lead to a more systematic exploration of trading opportunities.